 Today's Development Diary by ManoDeZombi[pdxint.at]Olá everyone and welcome to another dev diary for La Resistance! Let me begin by introducing myself: My name is Manuel, I’m from Spain and I joined Paradox as a Content Designer for HOI a couple of months ago (just on time to attend PDXCON, yeah!).I’ve been working on the implementation of Portugal for La Resistance. The original design of the focus tree was made by Portuguese professor Pedro Santos. He came with what I consider to be a really interesting idea, where the political branch of the tree has multiple possible interactions with the Spanish Civil War.While I worked on Portuguese Events and Decisions, the whole tree was implemented by our producer, Vachon (big kudos to her!). We tweaked the design of the Focus Tree a little bit, specifically the communist branch, which we felt was a bit dull compared to others, and the SCW-related branches to make them properly interact with Spain. Now I’m the one who will polish the tree and will attempt to get rid of all those lovely bugs our great Betas are reporting. Talking about Betas, our freelance artist @Indyclone77 is the one to blame for all the wonderful Portuguese event pictures and new icons you are about to see in the focus tree and national spirits, he has done an amazing job not only in making all that cool art, but also in providing crucial feedback during the development, so big kudos to him as well!Before going on, please note that balancing is still a work in progress, so there may be changes in what you are about to see.So I’d like to start talking about the National Spirits Portugal will start with in 1936:
Today's Development Diary by ManoDeZombi[pdxint.at]Olá everyone and welcome to another dev diary for La Resistance! Let me begin by introducing myself: My name is Manuel, I’m from Spain and I joined Paradox as a Content Designer for HOI a couple of months ago (just on time to attend PDXCON, yeah!).I’ve been working on the implementation of Portugal for La Resistance. The original design of the focus tree was made by Portuguese professor Pedro Santos. He came with what I consider to be a really interesting idea, where the political branch of the tree has multiple possible interactions with the Spanish Civil War.While I worked on Portuguese Events and Decisions, the whole tree was implemented by our producer, Vachon (big kudos to her!). We tweaked the design of the Focus Tree a little bit, specifically the communist branch, which we felt was a bit dull compared to others, and the SCW-related branches to make them properly interact with Spain. Now I’m the one who will polish the tree and will attempt to get rid of all those lovely bugs our great Betas are reporting. Talking about Betas, our freelance artist @Indyclone77 is the one to blame for all the wonderful Portuguese event pictures and new icons you are about to see in the focus tree and national spirits, he has done an amazing job not only in making all that cool art, but also in providing crucial feedback during the development, so big kudos to him as well!Before going on, please note that balancing is still a work in progress, so there may be changes in what you are about to see.So I’d like to start talking about the National Spirits Portugal will start with in 1936:- Unreliable Army: Representing the poor state of the Portuguese army during the period of the First Republic, which historically led to a major reorganization in 1937, it provides some penalties to Division Organization, Recruitable Population Factor, War Support and Division Attack, so you want to get rid of this before entering any conflict (probably not the best idea to join the Spanish Civil War only to see how your disgusting Spanish enemies defeat your unprepared troops and occupy your precious mainland in a blink...).
- Unstable Republic: During its 16 years, the First Portuguese Republic saw the inauguration of nine presidents and 44 cabinet reorganizations. Even during the Ditadura Militar there were several failed coup attempts. In 1933, after Salazar’s creation of the Estado Novo and the new Constitution approved in a referendum, Portugal’s stability slowly increased (maybe the censorship system and the different police forces that repressed all kinds of dissidents also helped a little bit with that). So another no-good spirit applying penalties to your Daily Political Power Gain, Stability and Construction Speed. You will be able to remove it through the different political branches, and you will probably want to do it ASAP.
 Now let’s look at the Portugese Focus Tree and talk about the different paths a player can choose from:
Now let’s look at the Portugese Focus Tree and talk about the different paths a player can choose from: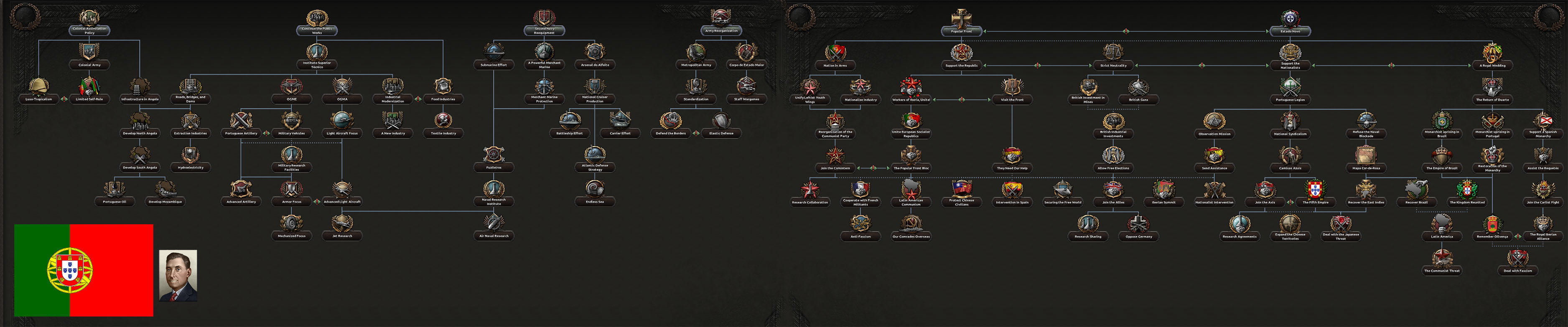
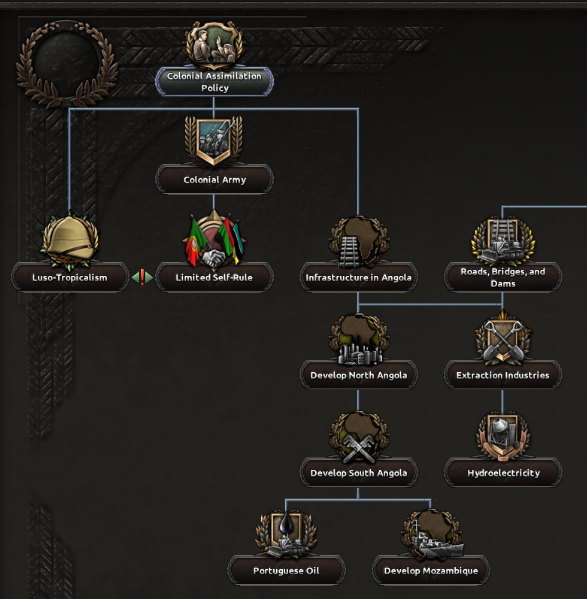
See an enlarged version of this image on the forumsAs you can see, the general structure varies a little bit from the standards of other trees, where you have clear separate branches for industry, military forces and politics.Let’s start with the colonial branch, shall we?Through the first focuses, Portugal will receive big bonuses to non-core manpower that will prove really useful in the early stages, since Portugal’s initial manpower is really low. The player can then choose between integrating the African colonies (which will also provide some extra manpower), or allowing them to form their own governments and puppeting them (something that will be appreciated by other democracies in the world).There is also a sub-branch that joins the industrial one, developing industry and infrastructure in the African colonies.
 Regarding Industry, by continuing the public works initiated by Salazar’s regime around the early 30s, Portugal will gain access to the first focus that will provide her first extra research slot (take into consideration that Portugal starts with only two research slots, so it seems just fair for her to get an early focus to fix that). The player can also choose between a fast development of the civilian industry receiving more factories or, with a slower approach, invest in future development getting some nice bonuses to industry research and construction speed.Portugal can also improve infrastructure and resource extraction industries on the mainland and, of course, there is a focus representing the construction of dams, something Iberian dictators liked very much to do.And then we have the military industry sub-branch, where the player can get (much needed) military factories and some useful bonuses to production and research for aircraft, vehicles and artillery. Make sure you don’t miss the extra research slot “hidden” between all these industrial focuses!
Regarding Industry, by continuing the public works initiated by Salazar’s regime around the early 30s, Portugal will gain access to the first focus that will provide her first extra research slot (take into consideration that Portugal starts with only two research slots, so it seems just fair for her to get an early focus to fix that). The player can also choose between a fast development of the civilian industry receiving more factories or, with a slower approach, invest in future development getting some nice bonuses to industry research and construction speed.Portugal can also improve infrastructure and resource extraction industries on the mainland and, of course, there is a focus representing the construction of dams, something Iberian dictators liked very much to do.And then we have the military industry sub-branch, where the player can get (much needed) military factories and some useful bonuses to production and research for aircraft, vehicles and artillery. Make sure you don’t miss the extra research slot “hidden” between all these industrial focuses!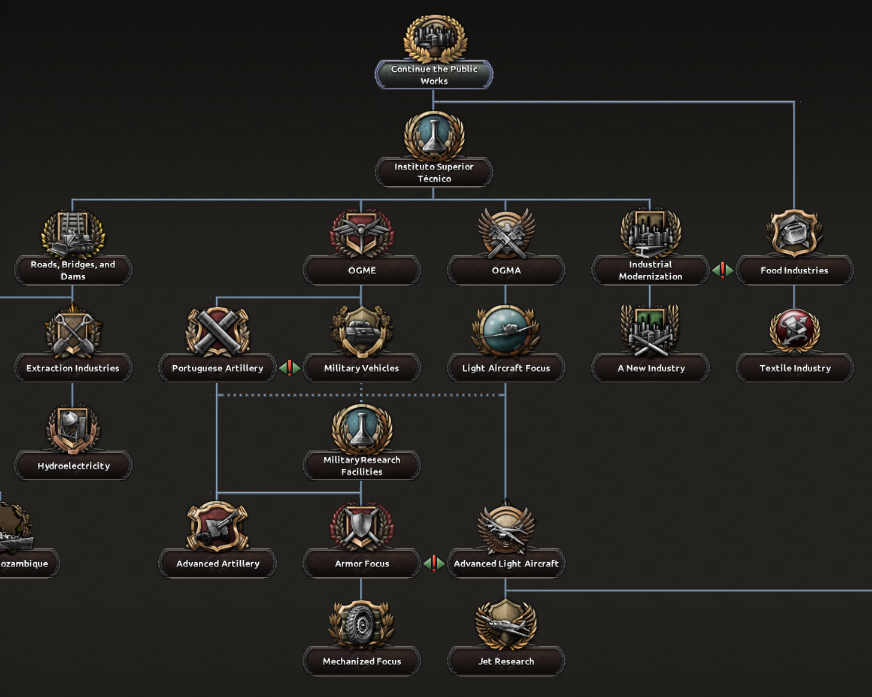 The first focus on the Naval Branch will unlock decisions to buy ships from either The United Kingdom or Italy. If they accept to build your ships (make sure you have good relations with them before activating the decision!), you will then be presented with three different options to choose from.
The first focus on the Naval Branch will unlock decisions to buy ships from either The United Kingdom or Italy. If they accept to build your ships (make sure you have good relations with them before activating the decision!), you will then be presented with three different options to choose from.
 The central and left sub-branches focus on Convoy protection and submarine warfare, providing a number of research bonuses for destroyers and submarine warfare, as well as adding a couple of dockyards to boost your naval production. These sub-branches then merge, eventually leading to a focus that unlocks Portugal’s third and last research slot (for a total of five).The right side of the naval branch is focused on the production of the big ships, as well as fortifying the vulnerable Portuguese possessions in the Atlantic Ocean and Asia.
The central and left sub-branches focus on Convoy protection and submarine warfare, providing a number of research bonuses for destroyers and submarine warfare, as well as adding a couple of dockyards to boost your naval production. These sub-branches then merge, eventually leading to a focus that unlocks Portugal’s third and last research slot (for a total of five).The right side of the naval branch is focused on the production of the big ships, as well as fortifying the vulnerable Portuguese possessions in the Atlantic Ocean and Asia. The Army Branch, although fairly small (don’t worry, you will find more military focuses under the Political Branch), will help Portugal to get its army in shape for the conflicts to come. The first focus removes that nasty Unreliable Army National Spirit and leads to some research and production bonuses in the next focuses. Finally, you will have to choose between building heavy fortifications in Lisbon, or creating a light fortification line along the coast.
The Army Branch, although fairly small (don’t worry, you will find more military focuses under the Political Branch), will help Portugal to get its army in shape for the conflicts to come. The first focus removes that nasty Unreliable Army National Spirit and leads to some research and production bonuses in the next focuses. Finally, you will have to choose between building heavy fortifications in Lisbon, or creating a light fortification line along the coast. Now, let’s take a general look at the whole Political Branch before getting deeper into each of the sub-branches:
Now, let’s take a general look at the whole Political Branch before getting deeper into each of the sub-branches: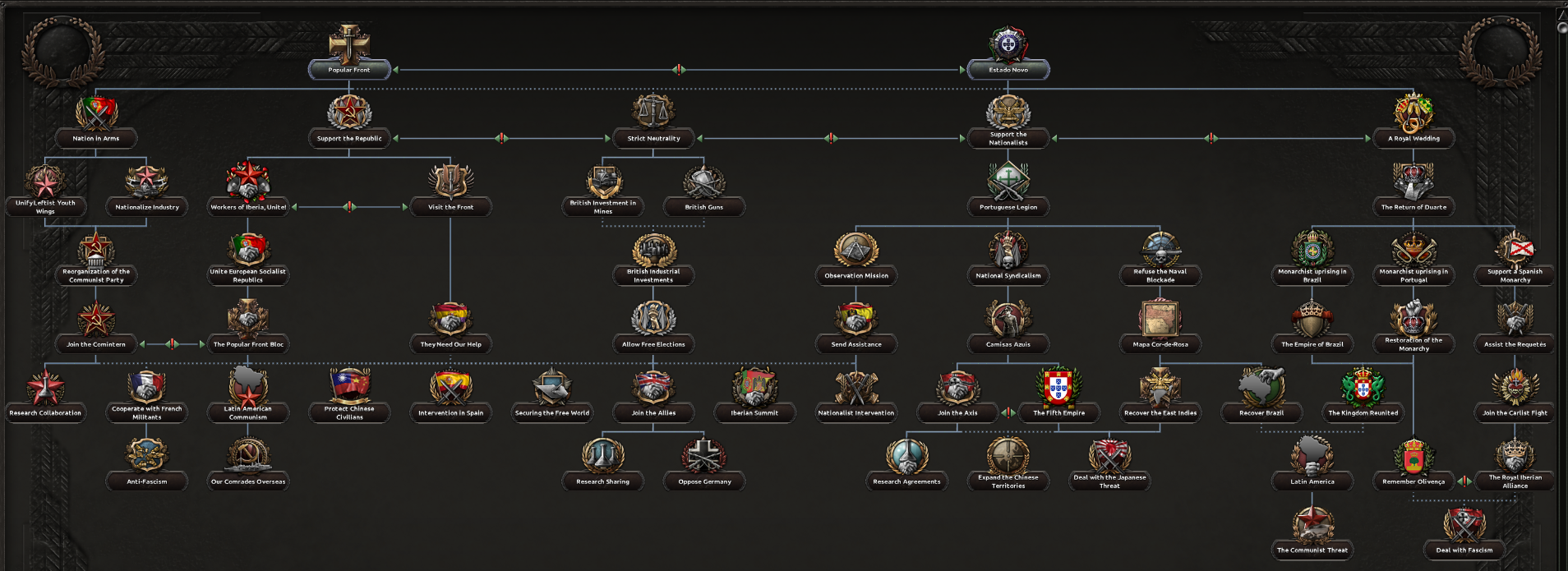
 In the right, we have the “cautious” approach to the Spanish Civil War. Here you won’t be able to join the SCW until you have swapped to a communist government. It’s a much slower approach, but after the war, you can pick different focuses to interact with foreign countries, including one that will grant you a war goal against Spain, in case their ideology is no longer desirable for you.
In the right, we have the “cautious” approach to the Spanish Civil War. Here you won’t be able to join the SCW until you have swapped to a communist government. It’s a much slower approach, but after the war, you can pick different focuses to interact with foreign countries, including one that will grant you a war goal against Spain, in case their ideology is no longer desirable for you. If you go with Strict Neutrality you won’t be able to interact in the SCW, but you will gain some nice boosts to your industry, production and Democracy support via the British, as well as some recurrent decisions to purchase equipment from them.
If you go with Strict Neutrality you won’t be able to interact in the SCW, but you will gain some nice boosts to your industry, production and Democracy support via the British, as well as some recurrent decisions to purchase equipment from them.

 In case you go with Estado Novo, you will have to choose between Strict Neutrality (mentioned above), Support the Nationalists and the Monarchist branch.Support the Nationalists, as its Republican counterpart, will allow you to support Nationalist Spain and send volunteers in the Spanish Civil War. You can join the SCW against the Republic in further focuses, and also intervene in Spain after the civil war if the Spanish government does not match your ideology.National Syndicalism will pave the way to become Fascist, leading to some interesting focuses: You can either join the Axis, or claim that Portugal will be the nation that finally unites the entire world under the same rule, ideology and faith (this will provide a powerful National Spirit, but it will also annoy some people around the globe).Refuse the Naval Blockade unlocks a decision for countries at war with the United Kingdom, by which they will use some of your convoys to carry supplies where they cannot reach, increasing their War Support and, of course, diverting the production of one of their factories to meet your needs.
In case you go with Estado Novo, you will have to choose between Strict Neutrality (mentioned above), Support the Nationalists and the Monarchist branch.Support the Nationalists, as its Republican counterpart, will allow you to support Nationalist Spain and send volunteers in the Spanish Civil War. You can join the SCW against the Republic in further focuses, and also intervene in Spain after the civil war if the Spanish government does not match your ideology.National Syndicalism will pave the way to become Fascist, leading to some interesting focuses: You can either join the Axis, or claim that Portugal will be the nation that finally unites the entire world under the same rule, ideology and faith (this will provide a powerful National Spirit, but it will also annoy some people around the globe).Refuse the Naval Blockade unlocks a decision for countries at war with the United Kingdom, by which they will use some of your convoys to carry supplies where they cannot reach, increasing their War Support and, of course, diverting the production of one of their factories to meet your needs.
 In the case of a Carlist Uprising happening during the Spanish Civil War, you can support your Monarchist friends in Spain and join the war against all those disgusting Communists, Socialists, Anarchists and Fascists (a lot of people to deal with in the Iberian Peninsula).
In the case of a Carlist Uprising happening during the Spanish Civil War, you can support your Monarchist friends in Spain and join the war against all those disgusting Communists, Socialists, Anarchists and Fascists (a lot of people to deal with in the Iberian Peninsula). And that’s all from me, I hope you enjoyed the dev diary and make sure to stay tuned for the next one. Anyways, we wish you all a merry Christmas and very happy New Year. See you all in 2020!
And that’s all from me, I hope you enjoyed the dev diary and make sure to stay tuned for the next one. Anyways, we wish you all a merry Christmas and very happy New Year. See you all in 2020!